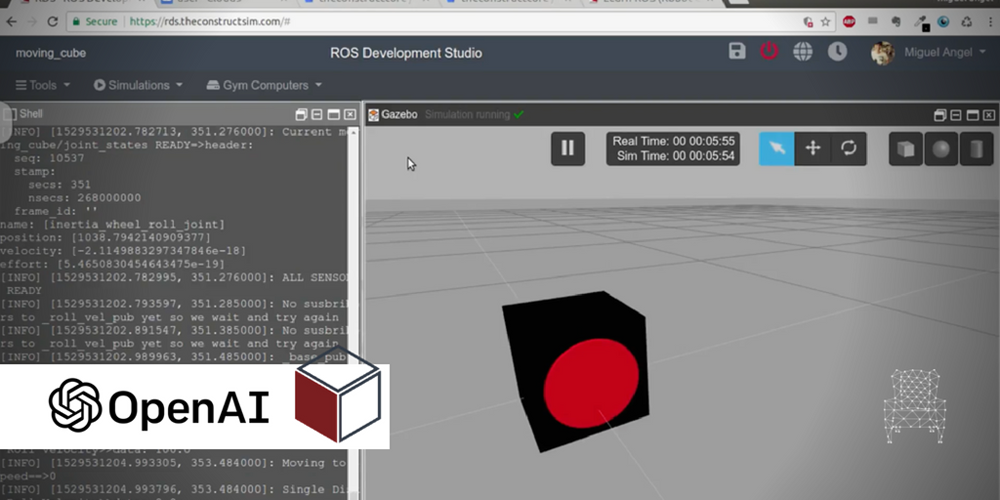
In this new ROS Project you are going to learn Step-by-Step how to create a moving cube and that it learns to move using OpenAI environment.
This second video is for learning the creation the basics of Reinforcement learning and how to connect to the various systems of the robot to get the state, perform actions and calculate rewards.
ROS Development Studio
OpenAi Course
Moving Cube Git:https://bitbucket.org/theconstructcore/moving_cube/src/master/
Moving Cube Training AI Git: https://bitbucket.org/theconstructcore/moving_cube_training/src/master/
If you didn’t follow up, please check the link below for the last post.
[irp posts=”9744″ name=”[ROS Projects] OpenAI with Moving Cube Robot in Gazebo Step-by-Step Part1″]
Step 1. Clone the simulation
In order to make sure we have the same project. Please run the following command
cd ~/simulation_ws/src git clone https://bitbucket.org/theconstructcore/moving_cube.git
NOTICE: please delete the previous code if you have problems to compile the code
In the /moving_cube/moving_cube_description/urdf/moving_cube.urdf file, please uncomment the following part. We’ll need this part to publish the odom topic.
<gazebo>
<plugin name="p3d_base_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_p3d.so">
<robotNamespace>/moving_cube</robotNamespace>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>50.0</updateRate>
<bodyName>cube_body</bodyName>
<topicName>odom</topicName>
<gaussianNoise>0.01</gaussianNoise>
<frameName>world</frameName>
<xyzOffsets>0 0 0</xyzOffsets>
<rpyOffsets>0 0 0</rpyOffsets>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
Step 2. Create a training package
To train the robot, let’s create a package for training under the catkin_ws/src
cd ~/catkin_ws/src catkin_create_pkg my_moving_cube_traning_pkg rospy
Then we’ll create a script folder inside the package and put a file called cube_rl_utils.py inside it with the following content
#!/usr/bin/env python
import time
import rospy
import math
import copy
import numpy
from std_msgs.msg import Float64
from sensor_msgs.msg import JointState
from nav_msgs.msg import Odometry
from geometry_msgs.msg import Point
from tf.transformations import euler_from_quaternion
class CubeRLUtils(object):
def __init__(self):
self.check_all_sensors_ready()
rospy.Subscriber("/moving_cube/joint_states", JointState, self.joints_callback)
rospy.Subscriber("/moving_cube/odom", Odometry, self.odom_callback)
self._roll_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/moving_cube/inertia_wheel_roll_joint_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
self.check_publishers_connection()
def check_all_sensors_ready(self):
self.disk_joints_data = None
while self.disk_joints_data is None and not rospy.is_shutdown():
try:
self.disk_joints_data = rospy.wait_for_message("/moving_cube/joint_states", JointState, timeout=1.0)
rospy.loginfo("Current moving_cube/joint_states READY=>"+str(self.disk_joints_data))
except:
rospy.logerr("Current moving_cube/joint_states not ready yet, retrying for getting joint_states")
self.cube_odom_data = None
while self.disk_joints_data is None and not rospy.is_shutdown():
try:
self.cube_odom_data = rospy.wait_for_message("/moving_cube/odom", Odometry, timeout=1.0)
rospy.loginfo("Current /moving_cube/odom READY=>" + str(self.cube_odom_data))
except:
rospy.logerr("Current /moving_cube/odom not ready yet, retrying for getting odom")
rospy.loginfo("ALL SENSORS READY")
def check_publishers_connection(self):
"""
Checks that all the publishers are working
:return:
"""
rate = rospy.Rate(10) # 10hz
while (self._roll_vel_pub.get_num_connections() == 0 and not rospy.is_shutdown()):
rospy.loginfo("No susbribers to _roll_vel_pub yet so we wait and try again")
try:
rate.sleep()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
# This is to avoid error when world is rested, time when backwards.
pass
rospy.loginfo("_base_pub Publisher Connected")
rospy.loginfo("All Publishers READY")
def joints_callback(self, data):
self.joints = data
def odom_callback(self, data):
self.odom = data
# Reinforcement Learning Utility Code
def move_joints(self, roll_speed):
joint_speed_value = Float64()
joint_speed_value.data = roll_speed
rospy.loginfo("Single Disk Roll Velocity>>"+str(joint_speed_value))
self._roll_vel_pub.publish(joint_speed_value)
def get_cube_state(self):
# We convert from quaternions to euler
orientation_list = [self.odom.pose.pose.orientation.x,
self.odom.pose.pose.orientation.y,
self.odom.pose.pose.orientation.z,
self.odom.pose.pose.orientation.w]
roll, pitch, yaw = euler_from_quaternion(orientation_list)
# We get the distance from the origin
start_position = Point()
start_position.x = 0.0
start_position.y = 0.0
start_position.z = 0.0
distance = self.get_distance_from_point(start_position,
self.odom.pose.pose.position)
cube_state = [
round(self.joints.velocity[0],1),
round(distance,1),
round(roll,1),
round(pitch,1),
round(yaw,1)
]
return cube_state
def observation_checks(self, cube_state):
# MAximum distance to travel permited in meters from origin
max_distance=2.0
if (cube_state[1] > max_distance):
rospy.logerr("Cube Too Far==>"+str(cube_state[1]))
done = True
else:
rospy.loginfo("Cube NOT Too Far==>"+str(cube_state[1]))
done = False
return done
def get_distance_from_point(self, pstart, p_end):
"""
Given a Vector3 Object, get distance from current position
:param p_end:
:return:
"""
a = numpy.array((pstart.x, pstart.y, pstart.z))
b = numpy.array((p_end.x, p_end.y, p_end.z))
distance = numpy.linalg.norm(a - b)
return distance
def get_reward_for_observations(self, state):
# We reward it for lower speeds and distance traveled
speed = state[0]
distance = state[1]
# Positive Reinforcement
reward_distance = distance * 10.0
# Negative Reinforcement for magnitude of speed
reward_for_efective_movement = -1 * abs(speed)
reward = reward_distance + reward_for_efective_movement
rospy.loginfo("Reward_distance="+str(reward_distance))
rospy.loginfo("Reward_for_efective_movement= "+str(reward_for_efective_movement))
return reward
def cube_rl_systems_test():
rospy.init_node('cube_rl_systems_test_node', anonymous=True, log_level=rospy.INFO)
cube_rl_utils_object = CubeRLUtils()
rospy.loginfo("Moving to Speed==>80")
cube_rl_utils_object.move_joints(roll_speed=80.0)
time.sleep(2)
rospy.loginfo("Moving to Speed==>-80")
cube_rl_utils_object.move_joints(roll_speed=-80.0)
time.sleep(2)
rospy.loginfo("Moving to Speed==>0.0")
cube_rl_utils_object.move_joints(roll_speed=0.0)
time.sleep(2)
cube_state = cube_rl_utils_object.get_cube_state()
done = cube_rl_utils_object.observation_checks(cube_state)
reward = cube_rl_utils_object.get_reward_for_observations(cube_state)
rospy.loginfo("Done==>"+str(done))
rospy.loginfo("Reward==>"+str(reward))
if __name__ == "__main__":
cube_rl_systems_test()
In this post, we’ll focus on the cube_rl_systems_test() function. The function uses the class to move the cube, get the observation, calculate reward and check if it’s done. To run it, you have to run the simulation first. Please go to Simulations->Select launch file-> main.launch
NOTICE: You have to unpause the simulation by clicking the arrow key in the simulation window
Then you can run the following command to run the script
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/my_moving_cube_training_pkg/script chmod +x cube_rl_utils.py cd ~/catkin_ws source devel_setup.bash rosrun my_moving_cube_training_pkg cube_rl_utils.py
You should see the cube moving around and the reward and the done state is calculated.
Edit by: Tony Huang
[irp posts=”9976″ name=”ROS Projects OpenAI with Moving Cube Robot in Gazebo Step-by-Step Part3″]



0 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks